Example 2: Q-D and Bairstow Combination
The following example demonstrates how to use the Q-D method in conjunction with the Bairstow method.
Example
Use a combination of the Q-D and Bairstow methods to find the roots of the polynomial
Procedure |
Press |
Display |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Select the program. | [ RUN ] { MTH } { --> } { ZRO } { Q-D } |
 |
| Enter the number of iterations | 25 { #it } { EOD } |
 |
| Select new polynomial | { YES } |  |
| Enter the degree of the polynomial | 5 { n } { EOD } |
 |
| Enter the coefficients | 1 { ENT } |  |
| 13 { ENT } |  |
|
| 62 { ENT } |  |
|
| 118 { ENT } |  |
|
| 97 { ENT } |  |
|
| 29 { ENT } |  |
|
| Proceed with program | { NO } |  |
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } | 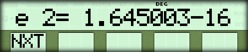 |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } | 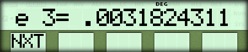 |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| { NXT } | 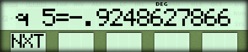 |
|
| { NXT } |  |
|
| Compute r and s values | { r/s } |  |
| Specify first and second roots to generate r and s | 1 { 1st } |  |
| 2 { 2nd } |  |
|
| View r and s | { EOD } |  |
| { NXT } |  |
|
| Select the Bairstow program | { NXT } { ESC } { ESC } { ESC } { BAI } |
 |
| Enter the number of iterations allowed | 25 { #it } |  |
| Enter the allowable error | .00000001 { err } |  |
| Proceed with program | { EOD } |  |
| Proceed with program | { NO } | 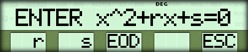 |
| Enter initial r and s | 10 { r } 29 { s } { EOD } |
 |
| View the real part | { Re } |  |
| View the imaginary part | { Im } |  |
| Proceed with program | { ESC } |  |
| { NO } |  |
|
| { NO } | 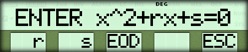 |
|
| View the roots | { EOD } |  |
| { R1 } |  |
|
| { R2 } |  |
|
| { R3 } |  |
|
The roots of the reduction polynomial are -5 + 2i and -5 - 2i. The roots of the remaining polynomial are all -1.
☚ Back


