Example: The Complex Functions Program
The examples below demonstrate how to use the Complex Functions program. The first example shows what to do when a calculation operates on more than two complex numbers. The second example includes the entry and conversion of polar numbers.
Example 1
Calculate ( ( 1 / ( 3 - 4i ) ) - √( -5 + 6i ) ) × 2.6i
Procedure |
Press |
Display |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Select the program | [ RUN ] { MTH } { PLX } |  |
| Enter -5+6i | 5 [ +/- ] [ x~t ] 6 { Xi } |  |
| Find √(-5+6i) | { EOD } { PRL } [ INV ] { X^2 } |
 |
| Store the result as Y and enter 3-4i for X | { X~Y } 3 [ x~t ] 4 [ +/- ] { Xi } |
 |
| Find 1/(3-4i) | { EOD } { ARI } [ INV ] { / } |
 |
| Use results in subtraction | { EOD } { ARI } { - } |  |
| Enter 0 + 2.6i as Y so previous result remains | 0 [ x~t ] 2.6 { Yi } |  |
| Multiply numbers and display the real part | { EOD } { ARI } { * } | 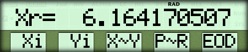 |
| Display imaginary part | [ x~t ] |  |
Conclusion
The result is 6.164170507 + i( -2.769987006 ).Example 2
Calculate sin( 100 ∠30° ÷ 40 ∠-90° ) and show the result in polar form.
Procedure |
Press |
Display |
|---|---|---|
|
|
||
| Select the program | [ RUN ] { MTH } { PLX } |  |
| Convert 40 ∠-90° to radians | 40 [ x~t ] 90 [ +/- ] [ CONV ] { ANG } { D-R } |  |
| Convert to rectangular and store result as Y | [ OLD ] { Xi } { P-R } { X~Y } |  |
| Convert 100 ∠-30° to radians | 100 [ x~t ] 30 [ CONV ] { ANG } { D-R } |  |
| Convert to rectangular | [ OLD ] { Xi } { P-R } | 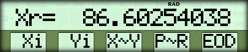 |
| Divide | { EOD } { ARI } { / } |  |
| Calculate the sine | { EOD } { CIR } { sin } |  |
| Convert to polar and show magnitude | [ INV ] { P-R } |  |
| Show angle (in radians) | [ x~t ] |  |
| Convert to degrees | [ CONV ] { ANG } [ INV ] { D-R } |  |
☚ Back


