Quadratic Equations
The { QAD } selection requires you to enter the coefficients of your equation. An equation in quadratic form has coefficients a, b, and c.:
Finding Quadratic Roots
Select { QAD } from the EXTENDED FUNC menu to display the QUADRATIC EQN menu.
- Enter the value of the a coefficient and select { a }.
- Enter the value of the b coefficient and select { b }.
- Enter the value of the c coefficient and select { c }.
- Select { XEQ }. One of the menus below is displayed.


- If the roots are real, display the two roots by selecting:
{ R1 } - the first real root.
{ R2 } - the second real root. - If the roots are complex, display the real and imaginary parts by selecting:
{ Re } - the real part.
{ Im } - the imaginary part.
Data registers 000, 001, and 002 are used to store both the inputs and the results. As the values for a, b, and c are entered, they are stored in registers 000, 001, and 002, respectively. After the two roots are determined, they are stored in registers 000 and 001. Register 002 contains a 0 if the roots are real and a 1 if the roots are complex. Therefore, the original inputs are no longer available in these registers.
Quadratic Example
Find the roots of the equation 4.2x2 + 0.22x + 8 = 0.Procedure | Press | Display |
|---|---|---|
| Clear display | [ CLEAR ] |  |
| Select quadratic roots | [ FUNC ] { QAD } |  |
| Enter value for a | 4.2 { a } |  |
| Enter value for b | .22 { b } |  |
| Enter value for c | 8 { c } |  |
| Determine roots | { XEQ } |  |
| Display real part | { Re } | 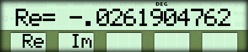 |
| Display imaginary part | { Im } |  |
-0.0261904762 + (1.379882591)i
-0.0261904762 - (1.379882591)i
☚ Back

